Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to reshape organizations in a manner that will be as influential as the smartphone revolution. Can you remember what the world was like before smartphones were introduced? Smartphones have changed human behavior and reshaped our communication, work, and leisure. What used to seem like a futuristic concept became an integral part of everyday life.
Today, Artificial Intelligence is at a similar transformative stage. Like smartphones, AI is set to revolutionize decision-making, efficiency, and personalization in organizations and human behavior. However, this technological advancement brings challenges including privacy concerns, possible bias, and a need to ensure transparency.
This is the first in a series of articles designed to make AI understandable and applicable for everyday organizational use. Let's start with the basics and explore how AI is increasingly becoming an essential part of the workplace landscape.
- Understanding Artificial Intelligence
- AI on the Hype Cycle
- AI’s Impact on Organizations
- The AI-Driven Future
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
The key feature of AI is its ability to learn from data and experiences, adapt to new situations, and handle complex tasks. These tasks include understanding spoken language, interpreting images or videos, solving problems, and making decisions. In other words, AI enables computers to do things that typically need human thought and judgement. That doesn't mean, however, that AI replaces humans. The AI creation process and any AI outputs should be reviewed and edited by a person.
Key Components of Artificial Intelligence
Understanding some basic concepts of AI such as machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotic process automation can empower organizational leaders to more effectively identify potential ways to leverage these technologies.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that involves training machines to learn from data. Rather than being explicitly programmed to perform a task, these systems are designed to analyze and interpret complex data, learn from it, and make informed decisions based on that learning. This is the technology behind personalized product recommendations, fraud detection systems, and predictive maintenance in industries.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) enables machines to understand and interpret human language. From chatbots that handle customer service inquiries to voice-activated assistants like Siri and Alexa, NLP allows computers to interact with humans in a more natural and intuitive way, enhancing customer engagement and service efficiency.
You may already be using NLP but don’t realize it. ChatGPT is an NLP application that performs language-based tasks like answering questions, engaging in conversation, and generating human-like text in response to the input it receives.
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) refers to the use of AI to automate repetitive and routine tasks. RPA is like having a digital workforce that handles time-consuming tasks such as data entry, processing transactions, or managing emails. This technology not only increases efficiency and accuracy but also allows your human workforce to focus on more strategic, creative tasks.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is the AI component that allows computers to “see” and interpret visual information from the world around them. This technology is used in various applications such as analyzing medical images for diagnostics, enabling self-driving cars to “see” their surroundings, and identifying potential intruders in security systems.
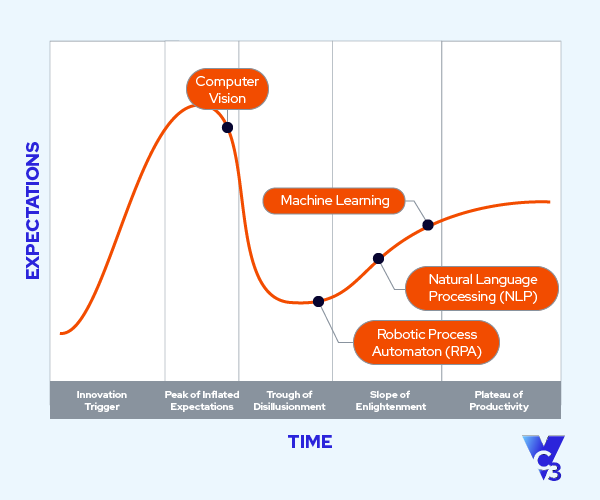
AI on the Hype Cycle
While there has been a lot of buzz about AI as applications like ChatGPT have become widely available, all AI technologies are not at the same position in their maturity. Assessing where AI technologies stand on tools like the Gartner Hype Cycle is essential for organizations to understand the challenges they may face in implementing the new technology.
The Gartner Hype Cycle provides a model to look at the varying maturity levels of technology and assesses their readiness for implementation. The model tracks technology lifecycles from inception to mainstream use, progressing through five stages.
- Innovation Trigger: This is where it all starts - a new tech idea pops up, sparking interest and lots of talk.
- Peak of Inflated Expectations: At this point, everyone's talking about it. Some early wins make people overly optimistic, but there are also some flops.
- Trough of Disillusionment: Reality check - the excitement cools off as some attempts to use the tech don't work out as hoped.
- Slope of Enlightenment: Here, people start figuring out the real deal - understanding where and how the tech can actually be useful.
- Plateau of Productivity: The tech becomes a regular part of life and business - it's proven, reliable, and more people use it effectively.
Interpreting AI's Position in the Hype Cycle
Understanding where AI technologies stand on this cycle helps to assess potential risks and opportunities. Technologies nearing the “Plateau of Productivity” are likely more stable and reliable, whereas those at the “Peak of Inflated Expectations” might pose greater risks.
- Machine Learning: Currently on the “Slope of Enlightenment” and approaching widespread practical application across industries.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Positioned on the “Slope of Enlightenment” and gaining effectiveness, especially in customer service areas.
- Computer Vision: In the late stages of the “Peak of Inflated Expectations” and evolving rapidly as it explores its full potential.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Transitioning toward the “Slope of Enlightenment” and increasingly adopted for automating routine tasks, overcoming initial skepticism.
AI’s Impact on Organizations
As we can see from the Gartner Hype Cycle, AI is not just a future possibility but a present reality with diverse applications. It's poised to reshape how organizations operate and how services are delivered. In fact, the practical AI applications that have so far been identified demonstrate AI's diverse utility. For example, AI can have an impact on:
- Business Operations: AI streamlines sales, marketing, HR, customer service, employee service, and finance, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.
- Municipal Services: AI streamlines operations and enhances public welfare by optimizing traffic flow, waste management, public safety, energy use, and emergency response.
Adopting AI in your organization isn't without its hurdles. One key challenge is ensuring you have the right talent to manage these AI systems. Another is on keeping all the sensitive data AI handles secure and private. Plus, organizations must maintain oversight on AI decisions to ensure they’re fair and unbiased. Navigating these aspects is crucial for using AI effectively and responsibly in your organization.
Despite the challenges, AI's impact offers opportunities for growth, efficiency, and improved services. Understanding and integrating AI strategically is key to thriving in an increasingly digital world.
The AI-Driven Future
Artificial Intelligence is not a passing trend but a pivotal force reshaping organizations. AI can address complex issues, improve customer experiences, and fuel growth. As we navigate this AI-driven future, understanding AI implementation challenges and its practical applications is key for organizations looking to transform with AI.
In this article, we've explored the world of Artificial Intelligence, relating its growth to the Gartner Hype Cycle and discussing its impact on organizations. We've highlighted the benefits and challenges of AI, setting the stage for deeper insights. Our next article will focus on how adopting AI can transform your organization, offering a glimpse into a future powered by these innovative technologies.
Join us as we continue to navigate the evolving landscape of AI.






